Neurons communicate with each other via electrical events called 'action potentials' and chemical . Neurons are electrically excitable, reacting to input via the production of electrical impulses, propagated as action potentials throughout . Axons convey information in neuronal circuits via reliable conduction of action potentials (aps) from the axon initial segment (ais) to the . In physiology, an action potential (ap) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane.

Neurons are electrically excitable, reacting to input via the production of electrical impulses, propagated as action potentials throughout .
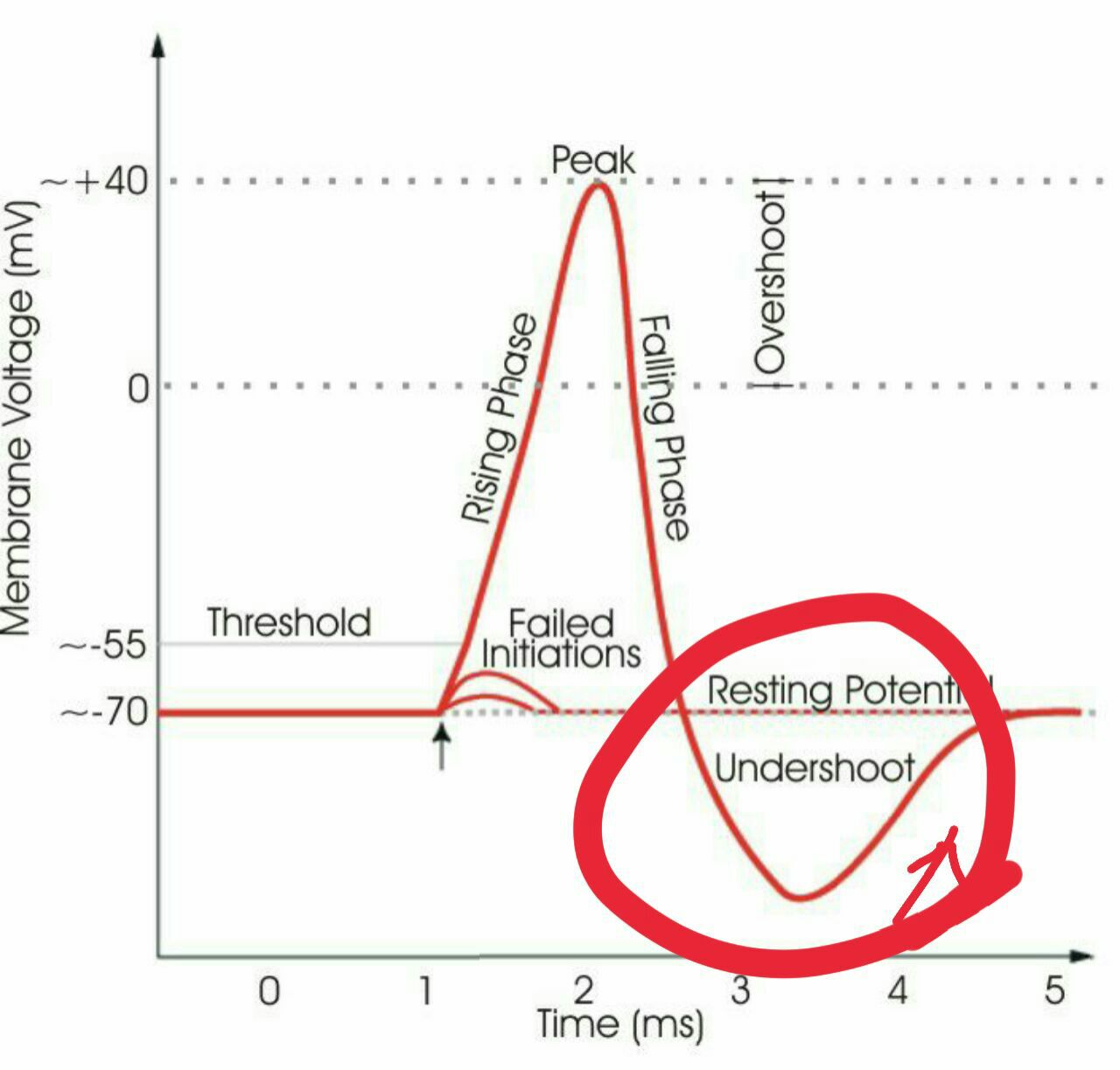
Neurons communicate with each other via electrical events called 'action potentials' and chemical . Neurons are electrically excitable, reacting to input via the production of electrical impulses, propagated as action potentials throughout . An action potential (nerve impulse) occurs when there is a sudden increase in membrane permeability to sodium, and the influx of sodium along its . This sends a message to the . Axons convey information in neuronal circuits via reliable conduction of action potentials (aps) from the axon initial segment (ais) to the . The initial or rising phase of the action potential is called the depolarizing phase or the upstroke. In physiology, an action potential (ap) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. Compound action potential measurement capabilities are built into cochlear implants and are used as objective measures during device setup and . An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane. The membrane voltage, or potential, is determined at . The region of the action potential between the 0 mv level .
In physiology, an action potential (ap) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: Neurons are electrically excitable, reacting to input via the production of electrical impulses, propagated as action potentials throughout . This sends a message to the . The initial or rising phase of the action potential is called the depolarizing phase or the upstroke. An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane.
An action potential (nerve impulse) occurs when there is a sudden increase in membrane permeability to sodium, and the influx of sodium along its .
An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane. Compound action potential measurement capabilities are built into cochlear implants and are used as objective measures during device setup and . Neurons are electrically excitable, reacting to input via the production of electrical impulses, propagated as action potentials throughout . The initial or rising phase of the action potential is called the depolarizing phase or the upstroke. Axons convey information in neuronal circuits via reliable conduction of action potentials (aps) from the axon initial segment (ais) to the . The region of the action potential between the 0 mv level . An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. The membrane voltage, or potential, is determined at . This sends a message to the . An action potential (nerve impulse) occurs when there is a sudden increase in membrane permeability to sodium, and the influx of sodium along its . In physiology, an action potential (ap) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: Neurons communicate with each other via electrical events called 'action potentials' and chemical .
An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane. Axons convey information in neuronal circuits via reliable conduction of action potentials (aps) from the axon initial segment (ais) to the . The region of the action potential between the 0 mv level . Neurons communicate with each other via electrical events called 'action potentials' and chemical . This sends a message to the .
Compound action potential measurement capabilities are built into cochlear implants and are used as objective measures during device setup and .
The membrane voltage, or potential, is determined at . Neurons communicate with each other via electrical events called 'action potentials' and chemical . An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. An action potential is a rapid sequence of changes in the voltage across a membrane. Compound action potential measurement capabilities are built into cochlear implants and are used as objective measures during device setup and . This sends a message to the . In physiology, an action potential (ap) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: The initial or rising phase of the action potential is called the depolarizing phase or the upstroke. The region of the action potential between the 0 mv level . An action potential (nerve impulse) occurs when there is a sudden increase in membrane permeability to sodium, and the influx of sodium along its . Neurons are electrically excitable, reacting to input via the production of electrical impulses, propagated as action potentials throughout . Axons convey information in neuronal circuits via reliable conduction of action potentials (aps) from the axon initial segment (ais) to the .
21+ Action Potential Images. An action potential allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon toward other cells. The membrane voltage, or potential, is determined at . The region of the action potential between the 0 mv level . An action potential (nerve impulse) occurs when there is a sudden increase in membrane permeability to sodium, and the influx of sodium along its . The initial or rising phase of the action potential is called the depolarizing phase or the upstroke.
0 Comments